SEO can be a confusing topic, with many conflicting opinions and a number of areas which are (to say the least) more than a little grey.
Well, grey is no use to anyone, so in this guide to SEO in 2016 I have explored over 80 common SEO questions and (in most cases) provided definitive answers. I have also included links to related articles (and videos) from other leading SEO experts and authorities where required.
The guide should serve both as a useful resource for anyone starting out in SEO and a good reference point for more advanced SEOs who are looking for clarification on specific areas of search engine optimisation.
Included are topics such as: –
- Current ranking factors
- Link building
- Google penalties
- Guest blogging
- Trust building
I will also keep the guide up to date as things change in the world of SEO, which they often do.
Contents
- 1 Is Content Really King?
- 2 Are Links Still The Primary Ranking Factor?
- 3 How Much Influence Does Google+ Have On Rankings?
- 4 Do Social Signals Influence Rankings?
- 5 Is Page Loading Time A Ranking Factor?
- 6 Does Bounce Rate Affect Search Rankings?
- 7 Is It Important To Vary Anchor Text When Building Links?
- 8 Is A Diverse Link Profile Important To Rankings?
- 9 Is Pagerank Still A Ranking Factor?
- 10 Are Links From Contextually Related Sites More Powerful?
- 11 Do Longer Articles Rank Better?
- 12 Do Nofollow Links Influence Rankings?
- 13 Does Google Prefer Sites Which Update/Add Content Regularly?
- 14 Will Duplicate Content Cause Your Site To Be Penalised?
- 15 Can You Rank A Webpage Without Text Content?
- 16 Does Google Have A Team Of Manual Reviewers?
- 17 Is Keyword Density An Important Ranking Factor?
- 18 Will Being At Number 1 Get You A Lot More Traffic Than Being At Number 2?
- 19 Can Big Brands Get Away With Things That Small Sites Can’t?
- 20 Will Selling Links Get Your Site Penalised?
- 21 Will Buying Links Get You Penalised?
- 22 Is Google Now Able To Look Beyond Keywords And Discern Meaning From Text?
- 23 Are Page Titles Still An Important Ranking Factor?
- 24 25. Will Links Passed Through A 301 Redirect Lose Pagerank?
- 25 Is There A Google Sandbox For New Sites?
- 26 Can You Rank A New Web Page?
- 27 Does Google Give A Rankings Boost To Fresh Content?
- 28 Does Guest Blogging Still Work For SEO?
- 29 Should You Nofollow Links From Guest Posts?
- 30 Does Linking To The Same Page Twice Divide The Pagerank?
- 31 Are Links From Links Pages Still Worthwhile?
- 32 Is Text Closer To The Top Of Content Seen As More Relevant?
- 33 Is Page Layout A Ranking Factor?
- 34 Does Google Lie?
- 35 Are Google Really Good At Detecting Spam?
- 36 Should You Submit Your Site To Google?
- 37 Will Submitting An Xml Sitemap Help Your Site To Rank?
- 38 Will Google Use Webmaster Tools Data To See Which Sites You Own?
- 39 Is Copying Your Competitor’s Links A Good Seo Tactic
- 40 Is Trustrank A Ranking Factor?
- 41 Is Pagerank Divided By The Total Number Of Links On A Page?
- 42 Does Google Look At The Text Surrounding A Link To Determine Relevancy
- 43 Do You Need Lots Of Anchor Text Links To Rank For A Phrase?
- 44 Will Semantically Correct Code Improve Your Rankings?
- 45 Will Using Query Strings In Urls Hurt Your Rankings?
- 46 Are Keywords In URL A Ranking Factor?
- 47 Are Keywords In Domain A Ranking Factor?
- 48 Does Google Penalise Affiliate Sites?
- 49 Should You Mask/Cloak Affiliate Links?
- 50 Is Internal Link Structure Important?
- 51 Should You Link To Your Home Page Using A Target Keyphrase?
- 52 Do One Way Links Have More Value Than Reciprocal Links?
- 53 Should You Only Link Out To Websites With Higher Pagerank Than Yours?
- 54 Do Links To External Sites Help Relevancy?
- 55 Does Google Rank Pages With Video Content Higher
- 56 Will Using Google Adwords Improve Your Organic Rankings?
- 57 61. Will Google Use Information From Your Analytics Against Your Site?
- 58 Will Mobile Friendly Sites Rank Higher?
- 59 Are Directory Submissions Still An Effective Seo Tactic?
- 60 When You Purchase An Expired Domain Name Is The Link Profile Reset?
- 61 Is Broken Link Building An Effective, White Hat Seo Tactic?
- 62 Will Putting Your Physical Address On Each Page Help With Local SEO?
- 63 Should Your Site Contain A Privacy Policy?
- 64 Can Google Follow Javascript Links?
- 65 Can Adsense Ads Hurt Your Rankings?
- 66 Will Google Cap The Amount Of Organic Traffic Your Website Receives Each Day?
- 67 Will Alt Text On Images Help Your Rankings?
- 68 Can Google Read CSS?
- 69 Do Dot Com Sites Rank Higher Than Country Specific Domains?
- 70 Does Google Prefers Web Pages With A .Html Extension?
- 71 Will Google Read Your Gmail To Find Out What You Are Up To?
- 72 Clickthrough Rate (Ctr) From Search Results Is Used As A Ranking Factor
- 73 Is Length Of Domain Registration A Ranking Factor?
- 74 Are Hyphenated Domains Best For SEO?
- 75 Are Hyphenated Urls Best For Individual Pages?
- 76 Are Short Urls Better For Rankings?
- 77 Is Including Your Brand Name In Your Page Titles Good For SEO?
- 78 Do You Need X Number Of Links To Rank?
- 79 Is There More Traffic To Be Had From Longtail Searches Than Main Keywords?
- 80 Should You Limit The Number Of Links On A Page To 100?
- 81 How Often Does Google Update Their Index?
- 82 Over To You!
Is Content Really King?
Content is king is a mantra that is probably repeated more often than any other in the world of SEO, so is a good place to start.
Google are continually telling us that to rank our sites we should focus on creating quality content. So will writing an amazing article be enough to bring the mountain to Mohammed?
Well, this may be a surprise, considering how much I bang on about the importance of quality content… but not exactly.
Your content is like your product and even the best products in the world need to be marketed. Everyone and his wife knows coca-cola, but they still spend billions of dollars a year on advertising don’t they?
Check out the chart below from Asymco which shows the advertising budgets of some of the world’s biggest brands.
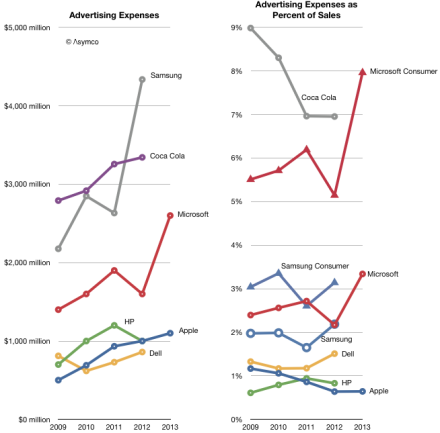
So, while it is completely true that your content should be exceptional, to generate traffic to it you have to get that content in front of the right eyeballs. It won’t magically rank on its own (unless you are looking at ranking for very noncompetitive phrases).
With that in mind, I’m actually going to say that content is not king. It may be the meat of the SEO pie, but without some focused marketing behind it, you’re just going to have boring old stew on your plate and not a crusty, tender, traffic (and sales) pie.
[Tweet “Content is *not* king (it’s the meat of the SEO pie)”]Are Links Still The Primary Ranking Factor?
When I started writing this guide back in January there was some debate about whether social signals were becoming more important than links for rankings. Well, that debate was put to bed at the end of January when Matt Cutts released a video (below) stating clearly that google does not currently use social signals (i.e. tweets, facebook likes etc) as a ranking factor.
You can read searchengineland’s initial reaction to the video and it’s implications here.
Matt also released a video at the beginning of May in which he stated that google won’t be devaluing links any time soon: –
I would expect for the next few years we will continue to use links in order to assess the basic reputation of pages and of sites.
It is safe to assume that links continue to be the most powerful ranking factor, although I must caveat this by saying: –
- They have to be the right kind of links
- Links alone will not guarantee rankings
More on this as the article progresses.
I should also mention that a recent google patent would suggest that citations (i.e. non linked brand mentions) are also becoming increasingly important to SEO (especially local SEO).
[Tweet “Links are still the most imporant #SEO ranking factor”]How Much Influence Does Google+ Have On Rankings?
Google+ shares and plus 1s do not currently influence rankings.
You might want to read Eric Enge’s detailed study of of google plus impact on on search rankings. Eric’s conclusion was that: –
In our study, and in my opinion, Google Plus Shares did not drive any material rankings changes (of non-personalized results) that we could detect
Do Social Signals Influence Rankings?
As discussed above (under links being the primary ranking factor), google have clearly stated that social signals do not currently influence search rankings directly. What social does do however is: –
1) Drive referral traffic
2) Increase visibility – an article going viral on social media will get in front of more eyeballs, which can lead to more links
So, social signals do have a huge indirect affect through the links they can subsequently generate, but in terms of direct influence the statement is false.
[Tweet “Social signals do not influence #google rankings (well not directly…)”]Is Page Loading Time A Ranking Factor?
Does google use page loading time as a ranking factor?
Well, this is another one that I can answer definitively as google came out directly and told us that it does – way back in 2010.
The post from google does say that it affects less than 1% of queries, but there can be no doubt that optimising your site’s load time will definitely be good for your site’s SEO and also of course your visitors.
For a more in depth study of page loading time as a ranking factor, see this article by Mark from Zoompf on the moz blog.
[Tweet “Page loading time is an #SEO ranking factor”]Does Bounce Rate Affect Search Rankings?
There is a belief among some SEOs that lowering the bounce rate of your site (that is the amount of people that click back without engaging with your page/visiting another page) will improve your search rankings.
Firstly, the bounce rate here generally refers to the one shown in your analytics account, which is not generally an accurate reflection of how useful a page has been to a user.
For example, an article on your site might cover a topic in its entirety and answer all the users questions about it. Now, if they leave your site without signing up/buying/completing whatever goal you have in mind, then this might not be great for you, but it’s not a good indication of whether or not your page was a good match for the query – more a sign that you need to look into your design/calls to action!
To clarify, unless you tweak things, even if a user stays on your page reading your content for 10 minutes, assuming they then click back or close their browser, this will still register as a bounce in analytics.
I bet wikipedia has a pretty high bounce rate, yet it doesn’t seem to affect their rankings!
The good news is this is another one where google (or at least Matt Cutts) has come out directly and said that they don’t use analytics bounce rate as a ranking factor and it is generally accepted that this is the case.
This of course doesn’t stop the speculation, but I’m inclined to believe them on this, so would say that bounce rate is not a direct ranking factor.
Is It Important To Vary Anchor Text When Building Links?
Remember the good old (or bad old?) days of SEO, when all you had to do to rank for a keyword/phrase was get the most number of exact match anchor text links for that phrase?
Well, it’s safe to say those days are gone!
It was far too easy to game and although google bombing could be pretty funny (check out these brilliant examples!), things had to change.
So, since the launch of google Penguin in 2012, which penalised over optimisation, it is generally accepted best practice to vary your anchor text when link building and not go keyword crazy.
A mix of the following is good for a diverse distribution of anchor text (for a target phrase of ‘cheap watches’): –
- branded links (name of company/site), i.e. ‘Watch Store’
- partial/broad matches, i.e. ‘you can buy cheap watches’, ‘an inexpensive watch’
- exact keyword/phrase, i.e. ‘cheap watches’
- generic links, i.e. ‘click here’, ‘this site’ etc
- naked url links, i.e. http://www.watches.com
The perfect distribution of these types of anchor text is up for debate, but this article on search engine journal does a good job of looking into the backlink profiles of some high ranking sites and breaking them down.
Of course, if your site attracts editorial links (through creating great content) then you will naturally have a diverse mix of penguin safe anchor text!
Anyway, it is safe to say that is definitely important to vary your anchor text when building links.
[Tweet “Vary your anchor text to avoid #google penalties”]Is A Diverse Link Profile Important To Rankings?
Similar to the above, but going beyond just anchor text, there is a belief that you should vary the types of link in your site’s link profile.
Examples of some of the types of link you might have in your profile include: –
- Contextual links (from within content paragraphs)
- Bio links from guest posts
- Forum links
- Sidebar links
- Footer links
- Links from link pages
- Additional reading links at the bottom of articles
- Wiki links
- Social media/web 2.0 links
- Links from question/answer sites (i.e. yahoo answers)
- Press releases
- Comment links
- Mix of follow/nofollow links
- Mix of text and image links
The theory is that if all your links are, for example, coming from blogs then this doesn’t look natural and is likely to trigger a Penguin penalty.
It is generally accepted that this is true, however, beware of automated tools that will get you x amount of each type from low quality sites. While link diversity is definitely a ranking factor, quality is still the most important!
This article by Julie Joyce does a good job of explaining why link diversity is so important in the post penguin SEO world.
[Tweet “A diverse link profile is important for search rankings”]Is Pagerank Still A Ranking Factor?
Pagerank was what initially set google apart from the other search engines. Hopefully you will have an understanding of what pagerank is and how it accumulates, but if not have a read at this article by Danny Sullivan, which is pretty definitive.
In fact, here’s a neat infographic from zippycart.

Anyway, it certainly used to be the case that the higher your site’s pagerank, the higher you were likely to rank in the search engines for given queries.
To improve your site’s pagerank, you could get lots of links from sites with pagerank 1,2,3 etc… or get just 1 link from a high pagerank site (7,8,9 etc).
This led to a huge market in link sales, with links from high pagerank sites selling for silly sums of money – google obviously did not like this!
There was/is also a fundemental problem in that, while real pagerank is updated continuously, google would historically only roll out an update to it’s toolbar pagerank (the infamous green bar) every quarter or so. In the last year, these updates have become even less frequent – in fact, there were only 2 in 2013. You can see a full history of toolbar pagerank updates going back to 2007 here.
So, enough of the history lesson. Is pagerank still a ranking factor? Well, the short answer is yes. The long answer is a little more complicated…
Pagerank is still taken into account when calculating the rankings of a web page, but it is not the be all and end all any more. It is just one of around 200 or so ranking factors.
You will often find sites with (what appears to be) low pagerank, outranking sites with high pagerank, based on things like: –
- Relevance
- Topical Authority
- Social Media Shares
With regards to link acquisition, my advice is to go after links closely related to your niche whenever possible (and preferably those that will drive actual referal traffic), in preference to going after unrelated links with higher pagerank.
You can read more about this in my article here.
[Tweet “Pagerank is still important to #SEO”]Are Links From Contextually Related Sites More Powerful?
Ok, I have already touched on this above.
There are those who will argue that a link is a link, but there are also many (and I am one of them) who believe that google categorises sites based on topic/theme. This article by Bill Slawski covers this in detail and is an excellent read.
It is logical to assume that google can also determine the topic/theme of a query and give a rankings boost to sites which are within that same theme.
With this in mind, it is important to develop your authority within a niche and one of the best ways to do this is to be cited (linked to) from other sites (ideally authorities) within the same niche.
So, while any editorially given link is a good one, all things being equal I would prefer to receive a link from a site which was based on the same topic as the one I was trying to rank.
For more on this, read my article on how to develop your topical authority.
Do Longer Articles Rank Better?
My thoughts are pretty clear on this one – for several reasons.
1. Google Is Still (Fundimentally) A Text Based Search Engine
Since google indexes text content, it is logical that the more text you have on your website, the more chances you have of being found for a broad number of phrases.
Read my article on why the real traffic is in the long tail for more on this.
2. Long Documents Are More Likely To Be Authoritative (And Attract Links)
If you cover a topic in its entirety, then it is more likely to be an authority document. And authority documents attract links and shares!
3. Google Has Launched An ‘in Depth Articles’ Feature
During the summer google added an ‘in depth articles’ feature to its search results. This is specifically for detailed documents, which are authorities on a topic.
It is reasonable to assume that this will become more and more important over the next year as google tweaks/enhances the feature. Read more about it here.
4. I Know From Experience!
I have seen great results in my affiliate sites from writing high quality articles, running to between 2,000 and 3,000 words.
I covered this in detail in my post last year on growing a new niche affiliate site. So, the statement that longer articles rank better is (generally) true, however…
This does not mean you should create words for the sake of it! If 100 words exhausts the topic, then your content should be 100 words.
Remember, always write for your readers, not the search engines!
Do Nofollow Links Influence Rankings?
Ok, this is a contentious one…
The rel=nofollow attribute was introduced by google to combat spam, and in particular comment spam.
Technically the definition of nofollow is that google (and other search engines that support the attribute) should not follow the link and not count it when calculating pagerank/rankings. However…
While I think it is probably true that it does not affect pagerank directly there is a widespread belief that nofollowed links do have some influence on rankings. At the very least, a mixture of nofollow/follow (I know the second one doesn’t exist!) links will help to give your link profile a natural look, which is certainly a ranking factor.
In a real world example, I have seen increases in rankings after getting a link from an article on wikipedia. To clarify, all links from wikipedia have the nofollow attribute, but it would certainly appear that they are passing authority, if not pagerank. And we already know that pagerank is not the rankings factor it once was.
With the above in mind, for the last couple of years at least, I have not concerned myself too much about whether incoming links are ‘followed’ or not.
So, while Matt Cutts might say otherwise, I am inclined to believe that nofollow links do influence rankings. This experiment adds some weight to the argument.
Does Google Prefer Sites Which Update/Add Content Regularly?
Does google give a preference to sites that regularly add and update content?
Well, this is another one of those yes, but with a caveat answers.
Way back in 2003, google filed a patent named ‘Document scoring based on document content update’. This patent was so important that it spawned a number of child patents and has been used by google for a number of years.
There are a couple of factors at play, which make adding regular fresh content and updating your old content important for your site’s SEO.
1. Fresh Content Gets A Rankings Boost
Recently added (fresh) content gets a rankings boost in SERPs and is likely to appear nearer the top for a couple of days (before falling down or sticking depending on other factors).
2. More Content = More Text
Remember, the more content you have, the better chance you have of ranking for a number of queries.
To keep your site riding high at the top of the search results you will need a steady flow of links/social media shares etc. High quality, fresh content will attract these links.
4. Updating Your Old Content Keeps It Evergreen
Those detailed articles we talked about above, there’s no point spending all that time writing them if you don’t keep them up to date.
Keep your cornerstone content fresh and it will continue to attract traffic/shares and links.
5. Adding More Content Gives Internal Linking Opportunities
Whenever you add new content you have the opportunity to link back to older content, helping it to maintain its rankings/boost relevancy.
That Caveat…
So, overall fresh/updated content is good for SEO, but that is not to say you cannot rank well with a static site.
It’s just going to be more difficult to keep visitors engaged/coming back and keep those links coming in.
Will Duplicate Content Cause Your Site To Be Penalised?
Think you can copy and paste your way to success in internet marketing? Think again!
Since the first Panda update in February 2011, if you want your web pages to show up anywhere in the search results you are going to need to write (or have written for you) unique content.
Content theft was/is a huge problem – and often copied/scraped content would outrank the original source. Not good for google or its users.
Panda went a long way to ensuring that copied content would not rank, but it also targeted thin content, i.e. pages where there was not much text, or content was similar to other pages on the same site.
The harsh thing with Panda is that it went beyond penalising individual pages and slapped on site wide penalties when the amount of duplicate/thin content went past a tipping point.
While overall this was a good thing, it had the unfortunate side effect of torching the rankings of a number of innocent(ish) ecommerce sites overnight. No longer would a default manufacturer’s description, or a 15 word regurgitation of the product name cut the mustard.
Beyond product descriptions, in their out of the box format, most ecommerce systems have a number of duplicate content issues (category pages etc). You might want to read my guide to seo for ecommerce sites for more on this and how you can fix it.
So, duplicate content will affect the ability of a web page to rank and too much of it site wide will cause the entire website to be penalised.
Update 27/05/2014: With the recent release of Panda 4.0, cleaning up your site’s indexing by removing thin/duplicate pages should be a priority for your site’s SEO. Read my guide to removing pages from google’s index for how to do this right.
I will add one final point on this, that spun content is not unique content and while it might pass Panda, you’ll end up with even bigger problems!
[Tweet “Duplicate content will get your site penalised!”]Can You Rank A Webpage Without Text Content?
Interestingly, I’m going to (kind of) contradict what I have just said above…
While, for most sites/pages it is going to be pretty difficult to rank without text content, this can all be trumped when: –
a) The site is an authority/500lb gorilla
b) The page attracts enough links/shares/buzz
An example I always give for this is hp.com – they never have any content on their homepage… but they are Hewlett Packard. They can do what they want.
Video content can also rank well if it gets enough links.
[Tweet “You can rank a web page with no content…”]Does Google Have A Team Of Manual Reviewers?
While the vast majority of search is algorithmical, it is certainly the case that google has a team of manual reviewers with the power to issue penalties.
Here is web spam king Matt Cutts himself discussing the very issue…
Some things that are likely to trigger a manual review of your site include: –
- Adding too much content too quickly
- Building links too quickly
- Duplicate content
- Broken Links
- Just being in a trophy/competitive niche
While, if you are doing things properly you should have nothing to hide, you might want to read this article which goes into some detail on what causes google to manually review a site and how you can avoid it.
For more on what a google manual reviewer might be looking for when assessing the quality of a site, have a read at this.
Is Keyword Density An Important Ranking Factor?
Way back when dinosaurs roamed the earth and excite was still a player in the search market, it used to be that the more times you used a keyword (or phrase) on a page, the more likely it was to rank for that phrase.
This was referred to as keyword density.
With this being far too easy to game, penalties started to be issued for using a keyword too much and all sorts of weird and wonderful figures were then quoted as the ideal keyword density for a page – 1%, 2%, 7.352%….
The truth is that keyword density really doesn’t matter (at least not unless you are using a phrase too much).
I have never concerned myself with it and I have never had any issues with ranking a web page for a target phrase.
As long as you use the phrase at least once within your content then it will be able to rank for that phrase.
In fact, it could possibly rank without even containing the phrase (but that’s not great SEO practice).
Don’t believe me? Here’s Matt Cutts again…
…and here are the opinions of a number of leading SEO experts.
So put your calculator away and forget about keyword density!
[Tweet “SEO: Forget about keyword density!”]Will Being At Number 1 Get You A Lot More Traffic Than Being At Number 2?
Everyone wants to be number 1 on google for their trophy phrases, but does it actually make a difference whether you are number 1 or 2?
Well, the answer is yes, it does – quite a bit actually.
I covered this in my article on whether your website deserves to be number 1, but to recap…
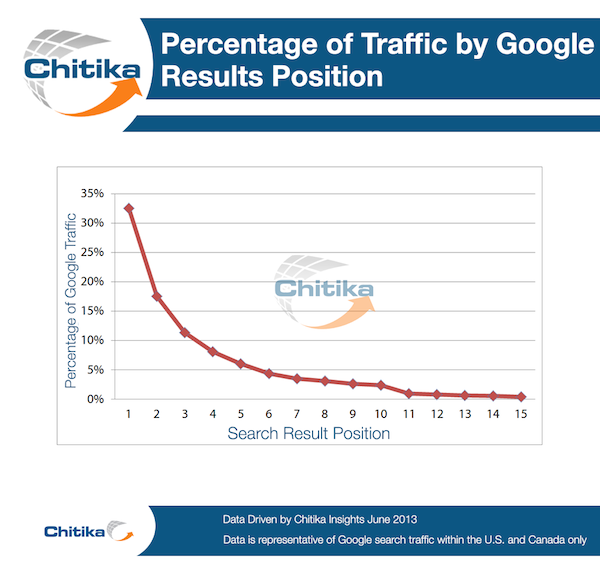
On average, the website in position 1 for a given search receives 33% of clickthroughs, while the website in position 2 receives just 18%. That’s a huge difference in traffic and is illustrated well by this chart from Chitika.
So, being at number 1 does make a difference.
[Tweet “Being number 1 on google will get you 33% more traffic than being at number 2!”]Can Big Brands Get Away With Things That Small Sites Can’t?
Ok, this is one where there is some disparity between what google says and what we actually observe.
The party line is that google does not give any preference to big brands and that they are subject to the same rules/potential penalties as any other site.
Certainly, there have been some high profile cases of big brands/sites losing rankings in the past, however…
When I looked into the SEO of a number of leading sites in the fashion niche, it was clear that some of their SEO practices were (at the very least) grey hat and (going by the book) liable to induce penalties.
I think what it comes down to though is that the big brands have such huge link profiles/social media shares/press coverage and other good signals that their trust factor ensures that they can get away with more at the grubbier end before triggering any penalties.
I guess a new site, if it could replicate this, would also be able to get away with the same, whether it was a household brand name or not.
Will Selling Links Get Your Site Penalised?
Yep, it will… …if you get caught!
Well, actually, you can sell links as much as you want, but to avoid google’s wrath you should add rel=nofollow to those links. Or not, it’s your site, just don’t be surprised if you lose your pagerank at some point.
This is common misconception – google doesn’t tell you what you should/shouldn’t do, it just tells you what not to do if you want to rank in their search results.
Will Buying Links Get You Penalised?
Yep… …again, if you get caught. Or if someone reports you.
My advice; don’t do it, but if you do… don’t buy a site wide anchor text link for heaven’s sake!!!
Is Google Now Able To Look Beyond Keywords And Discern Meaning From Text?
Ok, so we know that keywords density isn’t important, but google is still just a robot right, blindly indexing text? Wouldn’t it be cool if it could be more like a human and actually look at the meaning of the words on a page?
Well, it’s getting there!
The latest big change to google’s primary algorithm was google hummingbird and one of it’s primary aims was to do just this.
There are a couple of excellent articles on where this is all going, which it is well worth spending the time to have a read at: –
- Why Google’s New Hummingbird Algorithm Is Good News For Serious Content Creators (by Eric Enge on Copyblogger)
- Changing The Way Be We Think About SEO (by Jenny Halasz on Search Engine Land)
Suffice to say that it is happening, will get better and, as Eric Enge says, is good news for those who are writing high quality content.
Are Page Titles Still An Important Ranking Factor?
It’s easy to get bogged down in all the clever stuff with SEO – so much so that sometimes you just can’t see the wood for the trees and forget about the simple things.
And one of those simple things, which is still hugely important is; if you want to rank for a particular phrase, then make sure you use it in the title tag.
It’s been one of the biggest on page SEO factors since the start and continues to be so.
See my post on how to optimise your page titles for more.
[Tweet “Page titles are still one of the most important #SEO ranking factors!”]25. Will Links Passed Through A 301 Redirect Lose Pagerank?
Warning: This one can be a little difficult to get your head around!
When you move a webpage (or site) it is good SEO practice to redirect the old URL to the new one using a 301 (moved permanently) header redirect.
This will ensure that any old links pointing to the page will: –
1) Work
2) Continue to pass pagerank/authority
But does the 301 redirect pass the full amount of pagerank, or is there a damping factor, a dilution in pagerank?
Well, in a video this February Matt Cutts stated: –
The amount of PageRank that dissipates through a 301 is currently identical to the amount of PageRank that dissipates through a link.
So, what this would appear to say is that while a 301 redirect will lose pagerank, a direct link does too, so there is no difference. Here is the video.
We’ll take Matt Cutts’ word on this one and Barry Schwarz seems to agree, so that’s good enough for me!
Is There A Google Sandbox For New Sites?
It certainly used to be the case that when you launched a new site it would take a few months (at least) to start receiving any sort of decent search traffic.
This was commonly referred to as the ‘sandbox’ effect – there’s a good explanation of it here.
But is this still the case?
Well, in a search engine round table poll back in 2010, 67% of webmasters/SEOs certainly thought so.
For whatever reason there does seem to be a filter for new sites in place, but there could well be a simple explanation for this which has nothing to do with sandboxes or specific filters.
New sites are… new. They don’t have any links. They don’t have any social media shares/presence.
If a new site is genuinely excellent and launches with a bang, it is quite conceivable that it will quickly attract some good links/buzz which would allow it to rank, however…
A load of links coming in at once would potentially trigger Penguin and potentially cause a manual review, giving the impression of a ‘sandbox’ effect.
With this in mind it is difficult to say categorically whether or not the sandbox exists and I’m going to say this is unconfirmed.
Can You Rank A New Web Page?
This ties in with the point above.
While it is difficult to rank a brand new site/domain in the early months, it is certainly not impossible.
There is a good article here by Patrick Hare in which he explains how (when conditions are right) it can be done.
Obviously, the more competitive the niche, the harder it will be to break into – the SEO niche itself being a toughy!
My advice in the early days of a new site is to focus on creating content and building traffic through referals/social media. There’s huge traffic to be had when you look beyond google.
Does Google Give A Rankings Boost To Fresh Content?
We covered this one above in point 14 (google preferring regularly updated sites) and it is definitely true that google does give a rankings boost to fresh content (although sometimes not for long).
Does Guest Blogging Still Work For SEO?
Since this post was originally published google has taken some severe action against guest blogging, including the (frankly outrageous) de-indexing of MyBlogGuest.
Unfortunately, like many things in the world of SEO guest blogging has been abused by the spammers and guest blogging as a scaleable link building tactic is effectively dead.
When used correctly however guest blogging is still a great way to build your site’s authority and should be part of your overall SEO campaign.
Read my guide on how to guest blog in 2014 for more.
[Tweet “Guest blogging is not dead!”]Should You Nofollow Links From Guest Posts?
Ties in with the above and when you carry out a clean, effective guest blogging campaign you should not have to nofollow links from your guest posts.
Does Linking To The Same Page Twice Divide The Pagerank?
There are three lines of thinking with regards to multiple links to a single webpage from within content.
Let’s use the hypothetical example of 100 points of pagerank (just to illustrate!) to pass and 10 links on the page (to 9 different urls, i.e. 2 links to one of the web pages).
- The page with 2 links will receive 20 ‘points’ of pagerank
- The page will receive 11.11 ‘points’ of pagerank (i.e. the 100 points will be divided by 9) and in terms of anchor text (assuming the two links have different anchor text) each will only pass half the normal relevance.
- The page will receive 11.11 ‘points’ of pagerank and only the anchor text from the first link will be used as a ranking factor (i.e. the second link will be ignored).
There is no definitive answer on this (that I am aware of), so I am inclined to go with the second option. This makes it good practice to try and only link to each (internal) web page once from within content, but it’s not something I would get overly hung up on!
You can read some more discussion on it here.
Are Links From Links Pages Still Worthwhile?
Go on, admit it. You used to have one. A big spammy links page (or directory) on your site with links to every kind of site under the sun. Put there for the sole purpose of exchanging links with other sites.
Hopefully you don’t have that any more… but… Is there anything wrong with a well curated list of useful external resources, which will actually be of value to your visitors?
The answer is no. And with this in mind, why should a link from such a page on a site closely related to yours not pass any value?
The truth is (although feel free to disagree) that a links page is no different to any other and as long as it is not done for the purposes of manipulation and should pass pagerank/authority etc.
Would I rather have a link from within content? Yes.
Would I pass up a link from a links/resources page? No.
Do I ask for them? Yes. Has it ever done me any harm? No.
So there. Long live the links page.
Is Text Closer To The Top Of Content Seen As More Relevant?
This refers to the belief that google will give more prominence to keywords used in the opening paragraphs of a document.
Well, let’s think about that for a second… I used the first paragraph of this article to wish my readers a Happy New Year and I also talked about Christmas.
I’m going to have a bit of an issue if google uses that to determine the topic of this page aren’t I?
Just as keyword density is not an issue, neither is keyword positioning. Just write naturally.
Is Page Layout A Ranking Factor?
Ok, so while where keywords are used within a document may not be a ranking factor, the actual positioning of that content certainly is.
Google came out directly on their webmaster central blog and confirmed that they will look at the positioning of content when ranking webpages and, particularly where content is pushed below the fold there can be penalties.
You can read the full post (from January 2012) here, but I have included an extract which sums it up below:-
As we’ve mentioned previously, we’ve heard complaints from users that if they click on a result and it’s difficult to find the actual content, they aren’t happy with the experience. Rather than scrolling down the page past a slew of ads, users want to see content right away. So sites that don’t have much content “above-the-fold” can be affected by this change. If you click on a website and the part of the website you see first either doesn’t have a lot of visible content above-the-fold or dedicates a large fraction of the site’s initial screen real estate to ads, that’s not a very good user experience. Such sites may not rank as highly going forward.
With this in mind, you should be very careful about putting too many ads in your layout and (whenever possible) ensure that the beginning of your content is visible without any scrolling.
Ads should always be non intrusive and secondary to content.
You will find they convert better that way too!
Does Google Lie?
Google’s motto is ‘Don’t Be Evil’, but do they follow this practice themselves…
Well, with all the Edward Snowden/Prism/Privacy stuff it has certainly been an interesting year for them.
If you read certain Black Hat SEO sites, they will tell you that google tells out and out lies/spreads disinformation and that they are simply not as good at detecting spam as they would have you believe. You will probably notice that these sites are almost invariably promoting a black hat link building product/service…
My thoughts on this are that, while google is often less than clear on certain topics, they wouldn’t come out and tell out and out lies/falsehoods.
I guess they like to keep us on our toes as SEOs, by always leaving us slightly in the dark. Certainly, if you follow their webmaster guidelines (which are quite clear) then your site can/will rank and you will avoid penalties.
So, no, I don’t think they lie.
[Tweet “Does google lie?”]Are Google Really Good At Detecting Spam?
They may not be, but you better believe the net is closing…
Should You Submit Your Site To Google?
If someone ever offers to submit your site to google (and x other search engines) please print off the pdf of this post and hit them with it.
It’s not 1998 (if only it was).
Will Submitting An Xml Sitemap Help Your Site To Rank?
Google’s webmaster tools gives you the opportunity to submit an xml sitemap which contains all the pages of your site and even set a priority for each of the pages.
Should you do this? Maybe.
Will it help your site to rank? Not really.
Your site should be structured in such a way that every page is accessible (via a good internal linking structure) and google should be able to find the pages on its own accord.
If it can’t then take a look at your site’s architecture as a priority!
That being said, it’s not going to do you any harm and can sometimes get deep pages indexed quicker, so feel free to add one if you so desire.
Or have a cup of tea. It’s up to you…
Will Google Use Webmaster Tools Data To See Which Sites You Own?
This is a bit of an SEO scare story.
The theory goes that you should be careful which sites you have in your webmaster tools account as google will use this data to link your sites together and apply penalties across the board to them all if you are up to no good.
It will also use this data to devalue any crosslinking between the sites.
Opinion varies on this, but what I would say is if you are up to no good then it’s probably best to try and keep everything as separate as you can. Although, you will probably find that google will eventually link your sites together in other ways without relying on data from webmaster tools.
Is Copying Your Competitor’s Links A Good Seo Tactic
I was recently asked if the advice in Matt Woodward’s tutorial how to steal your competitor’s backlinks was sound. The answer is yes!
Looking into the backlink profiles of competing sites is one of the first things I do when taking on a new SEO contract.
One of the key things to look for are ‘hubs’ – that is sites/pages which are linking to 2 or more of your competitors. These are prime targets for outreach and are likely to consider linking to your site.
Matt advises to ‘use your head’ when analysing the links and this is good advice. Go after the strong links and ignore anything that looks a little dodgy.
So, copying your competitor’s links is without doubt a solid, SEO tactic.
You will need to combine this with other link building tactics to outrank them, but it is certainly a good place to start.
[Tweet “Stealing your competitor’s links is good for your SEO!”]Is Trustrank A Ranking Factor?
Trustrank was the buzz phrase in SEO in the final few years of the last decade, with many respected SEOs claiming that it would replace pagerank as the primary ranking factor.
So what is trustrank exactly?
Well, it’s a little complicated….
Matt Cutts has stated on several occassions that trustrank is not an actual specific metric that they use to rank your web page. You probably don’t have a specific trustrank score in the way that you might have a pagerank score.
But it is certainly true that your site can gain google’s trust through a combination of factors and that once you have this trust you will likely see an improvement in traffic, often a significant one.
Brian Dean does a good job of breaking down how to gain google’s trust in this article. I don’t necessarily agree everything on the list, but the key points are: –
- Develop on page trust – link out to authorities, include privacy policy/terms, lower bounce rate (hmmm…), cite references
- Look like a big brand – brand your site, detailed about page, active on social media, branded anchor text
- Trustworthy domain info – register for a 2+ years, public whois
- Trusted links – a strong, balanced link profile
It’s pretty much just a list of solid SEO advice, so I would say that while gaining the trust of google is very important to achieving traffic/rankings, trustrank is just really a combination of other factors/best practice and not really something we should say is a specific ranking factor in itself.
Is Pagerank Divided By The Total Number Of Links On A Page?
From a purely pagerank perspective it is certainly true that the less links there are on a page, the more pagerank each link will pass.
This of course does not take into account anchor text and contextual relevance (including the text surrounding the link – more on this in a moment).
Of course, the more pagerank a page has to pass, the more there is to divide between each link, so (while as we know pagerank is not the be all and end all!) technically a link from a pagerank 5 page with 20 outgoing links might still have more ‘juice’ than a link from a pagerank 2 page with 10 outgoing links.
Google have confirmed on several occassions that pagerank flows (and it is possible to sculpt the flow of this pagerank – see this article from Matt Cutts), so we will say that pagerank is divided by the number of links on a page.
Does Google Look At The Text Surrounding A Link To Determine Relevancy
While we know that anchor text is a ranking factor (although not something that should be aggressively pursued) does google also look at the text surrounding the link to determine relevancy?
Well, google filed a patent 10 years ago (in 2004) which would suggest that they do (read more in Bill Slawski’s article here).
Certainly if it does not give a positive boost, it is safe to assume that webspam would use this as a method to pick up manipulative linking.
Here is an example they used in a webmaster central blog post.
You would certainly think this would be pretty easy for them to pick up as spam.
I think it is safe to say that the text surrounding a link can be/is used by google as a ranking factor.
Do You Need Lots Of Anchor Text Links To Rank For A Phrase?
We kind of covered this in the section on the benefits of a diverse link profile for rankings, but it is certainly worthy of a point of its own.
Anchor text spamming is a favourite technique of black hat SEOs. It can certainly work for a short period – sometimes annoyingly so.
For example, a load of spam sites jumped into one of my niches once at a busy time. They crashed and burned out a couple of weeks later, but still did a lot of damage in the time they were there.
To be 100% clear, for sustained rankings/success you really should not worry about anchor text any more. If you focus on building links using white hat methods, you should naturally pick up some links containing your keywords. And too many anchor text backlinks = penguin penalty.
tip: Other sites will often link to you using your post/page title as the anchor text… another good reason to make sure your keywords are in there.
Even if you don’t have any links with the anchor text you are looking to rank for, assuming your site has enough authority it will still be completely possible to rank for that phrase.
Given the choice, branded links win every time. This article from Patrick Altoft does a good job of explaining why.
[Tweet “Branded links beat anchor match links every time!”]Will Semantically Correct Code Improve Your Rankings?
Does google give a rankings boost to well written, standards compliant code?
Well not really. Google has said on a number of occasions that as long as it can index the page it will be able to rank it.
Basically, if your page can display properly in a browser it will be able to rank.
There are of course lots of other good reasons to write standards compliant, semantically correct code other than SEO.
Will Using Query Strings In Urls Hurt Your Rankings?
While there are definite SEO (and user) benefits to rewriting URLs, google is perfectly capable of indexing naked URLs with query strings and there should be no ‘points off’ for using them.
Google have actually advised in the past that if your site is currently using naked URLs and is ranking well, then you shouldn’t change them for changes sake.
Are Keywords In URL A Ranking Factor?
Every list of ranking factors I have seen has included keywords in URL as a factor, however, the actual difference this makes these days is probably very marginal (it’s too easy to manipulate).
Certainly you shouldn’t spam and should just include two or three keywords at a maximum.
Are Keywords In Domain A Ranking Factor?
Just like keywords in URLs, the weighting of keywords in domains as a ranking factor has significantly decreased over the past couple of years.
It used to be the case that if you wanted to rank for a specific phrase, then grabbing the .com for those keywords (i.e. pinkelephants.com) would pretty much guarantee you to pop up at number 1.
This was clearly a flaw in the algorithm and in September of 2012, google rolled out their exact match domain update, which significantly decreased the weighting of keywords in domains and closed this loophole.
While having a keyword or two in your domain is not necessarily a bad thing, best practice these days is to think of branding first and keywords second.
That being said, depending on other factors and assuming your site has enough trust/authority, it is probably still a slight ranking factor, so we will say that it is true..
Does Google Penalise Affiliate Sites?
So, does google hate affiliate sites? No, of course not!
Whether your website is a blog, an ecommerce site or a price comparison site it has exactly the same potential to rank as any other.
What google (and specifically Panda) hates is thin sites/pages with low quality (or scraped) content and unfortunately a lot of affiliate sites happen to fall into this bracket.
When monetising a site through affiliate marketing you must create something of value – a resource that will benefit your visitors and is not simply a gateway to merchant sites.
Look at some of the biggest .com names around and you will find many of them use affiliate commissions as their primary source of revenue.
Here are some examples of affiliate sites that are doing things right and receive huge traffic from google: –
- Moneysupermarket.com
- Lastminute.com
- HotUKDeals.com
You can also read my guide to growing a new affiliate site.
[Tweet “Google does not hate affiliate sites!”]Should You Mask/Cloak Affiliate Links?
While google doesn’t have anything against affiliate sites, it is generally accepted best practice to mask/cloak your affiliate links with a ‘pretty url’.
You should also add the nofollow attribute to any affiliate links as technically these are paid links and should not pass pagerank.
Joost De Valk has a pretty good guide on why cloaking your affiliate links is good practice and how to do it right here.
Is Internal Link Structure Important?
As previously pointed out, google has confirmed that pagerank flows and as such it is possible to control the flow of that pagerank through your site. This is commonly referred to as pagerank sculpting.
A good internal structure will do several things: –
- Ensure every page on the site is spiderable (linked from other content)
- Create a hierarchical structure with ‘hub’ pages
- Ensure more links/pagerank flows to important pages
Sorting out internal link structure is one of the fundamentals of on-site SEO and fixing bad internal linking can do wonders for improving a websites rankings.
One thing to note is that (since 2009) you should not use the rel=nofollow attribute as a method for sculpting pagerank as the ‘juice’ for these links will be lost and not divided between the ‘followed’ links.
For more on this and some good tips read this article by Danny Sullivan, which is a few years old but still very relevant.
Internal linking is so important for SEO and is something I’m going to write up a full post on it, but for now here are a couple of good resources.
- 9 Pro Tips For Developing A Killer Internal Link Structure (searchenginewatch)
- Internal Links (Best Practices) – Moz
Should You Link To Your Home Page Using A Target Keyphrase?
One of my first pieces of advice for an SEO client (and something I practiced on my own sites) used to be to change the anchor text of those ‘home’ links to a phrase they wanted to rank for.
This used to work really well. Until about 2006/2007…
These days, if anything, using anchor text instead of generic phrases is more likely to get your site penalised than give any sort of boost.
Rand Fishkin ran some tests and wrote up quite an extensive article about it here. Rand concludes that while there is a slight positive impact for using anchor text for internal pages, but definitely not for the homepage.
Although linking to a page like our Web 2.0 Awards with the anchor text “web 2.0,” for example, appears to provide a positive nudge, the same does not hold true if I link to the homepage of SEOmoz with the anchor text “SEO.” In fact, for those who put a great deal of time into optimizing their links back to their homepage to say “new york apartments” or “antique rifles” rather than “home,” I’d test whether modification of the link anchor text has any adverse rankings impact. In my recent experience (on a few different sites), the answer is no.
So, stick to using ‘Home’ for your home links – it’s better for users and better for your search rankings.
Do One Way Links Have More Value Than Reciprocal Links?
I don’t get hung up on whether my inbound links are one way or not and neither should you.
Should You Only Link Out To Websites With Higher Pagerank Than Yours?
Another piece of outdated advice, but one that is still followed by many webmasters.
The only consideration when linking out should be the quality of the page you are linking to (and the site itself) and whether it gives additional value to your users.
Do Links To External Sites Help Relevancy?
Linking out to authorities in your niche is generally accepted to assist with your sites theming/relevancy.
Does Google Rank Pages With Video Content Higher
While it is certainly true that video content can rank very well (particularly youtube hosted vids when well optimised), I wouldn’t say that there is any particular SEO advantage in having video content on a webpage.
Well, in saying that… Good video content is great for your users and very shareable/linkable, so I guess while the video being on the page might not score extra points, the links that video might bring in will!
So, no direct boost, but certainly good to have!
Will Using Google Adwords Improve Your Organic Rankings?
As I mentioned above, google have always been very clear that they do not allow advertising to influence their organic results.
If someone tells you otherwise they either badly informed. Or lying.
I have actually taken phone calls from dodgy SEO companies in the past who have advised me that if I spend money using their adwords services it will improve my organic listings.
Needless to say I set them straight and they didn’t call me again…
Here is Matt Cutts answering this very question.
So, no rankings boost for spending big bucks on adwords.
61. Will Google Use Information From Your Analytics Against Your Site?
There is a widely held belief/concern that google will use certain data collected from analytics as a factor when ranking your website.
We already discussed (and discounted) bounce rate above, so what other data might google use? Well some of the ones people worry about are: –
- Number of pages per visit (a sign of engagement)
- Time/duration of visit
- Returning visitors (a sign that the content is ‘sticky’)
While it is clear to see how this could be used, Matt Cutts answered the question in this video back in 2011.
Webspam definitely hasn’t used google analytics data (to the best of my knowledge) and other places in google don’t either. Because we want people to just feel comfortable using it and… use it!
So relax, google will not use your google analytics account against you!
Will Mobile Friendly Sites Rank Higher?
Mobile browsing is huge and is only going to get bigger. You may well be reading this article on your phone right now.
Just under 15% of my traffic in December was on mobile, which would tally with this article from mashable last August revealing that 17.4% of web traffic is now mobile.
So, it is clear from a usability angle you want your site to display well in mobile (I recommend a responsive layout), but will having a mobile friendly site improve your organic search traffic?
Well, at Pubcon 2013 Matt Cutts stated:-
“if you haven’t developed mobile – you need to start look at it”
This is pretty close to a confirmation that it is (or soon will be) a ranking factor, so making sure your site is mobile friendly should definitely be a priority.
Certainly it stands to reason that google would rank mobile friendly sites higher on mobile searches.
Are Directory Submissions Still An Effective Seo Tactic?
Back in the day, submitting your site to a load of directories was a good way to boost your link popularity/pagerank, obtain some targeted anchor text and grow your traffic.
There was also loads of neat automated software that would do this for you… good times.
Nowadays however, where relevancy and high quality links are everything these sort of link blasts will inevitably get your site penalised.
So are directory submissions as an SEO tactic dead? Well, not exactly…
There are still some high ranking directories that will pass (at least some) authority to your site.
Directories like yahoo (if you can afford it) and DMOZ (if you can get a listing!) will still directly help and also contribute to a diverse link profile.
Also, highly targeted, niche specific directories can be a gem if you can find them. Like everything else it’s all about quality.
Check out point 7 on this great list of untapped backlink resources by Brian Dean for some good advice and a few nice directories to look into.
[Tweet “Directory submissions can still help your site’s SEO!”]When You Purchase An Expired Domain Name Is The Link Profile Reset?
I must admit that this is one that I am a little grey on. It is not something I have practiced before (as I believe in building your own brand/identity), so I can’t write using my own experience (although could make for an interesting future case study…).
A common SEO practice when launching a new site is to grab an expired domain name (with a decent backlink profile) instead of registering a brand new address. The theory is that you will then gain the benefit of the backlinks to the old site and will not be starting ‘from scratch’.
There is however a belief among some SEOs that when a domain expires the link profile is reset and that old links will no longer pass value when the domain is reactivated.
This makes sense to me as, if a link is a citation (or a vote) then how can that citation still be trusted when the content/purpose of the site may well have changed since the domain was reactivated?
But…
There are a lot of people buying expired domains and reporting good results using the tactic. This thread on seochat has several such claims and some interesting discussion.
I have trawled through a number of articles and discussions and the most common viewpoint seems to be that the new site will probably lose pagerank/some rankings after a few weeks, but that (assuming the old inbound links stay in place) then the pagerank/rankings will probably come back at some point in the future.
Barry Schwarz doesn’t appear to be 100% sure either (the question was regarding 301 redirecting expired domains, but the principal is the same)…
(1) Typically, Google may reset the value of a domain name when it expires. But not always.
(2) So you may or may not adopt the benefits and the negatives from that domain name if you 301 it.
(3) You can pick up some of his old customers by redirecting it to your site.
Of course, regardless of any actual ranking boost, if an expired domain has strong backlinks in place these might drive actual referal traffic, but this would only be useful if the new site is similar to the old one. No point in traffic that doesn’t convert!
I’m going to say this is unconfirmed, or certainly not crystal clear. If you have tried this out yourself I would be very interested to hear your results, so please leave a comment.
Is Broken Link Building An Effective, White Hat Seo Tactic?
If the question of whether an expired domain’s link profile is reset is up for debate, this next related point is one which I am very clear on.
Broken link building is the tactic of finding links broken links on web pages and contacting the webmaster to inform them of this and try and nab a link to your own (related) site in the process.
It is one of my favourite tactics and one which I have used to grab very strong links in the past. As I said above, asking for a link is not black hat and broken link building is a win win for the owner of the site with the broken link and for you as a marketer.
My tutorial on broken link building will tell you all you need to know about how to make the most of broken link building as an SEO tactic.
Definitely something that should be part of any white hat SEO campaign.
Will Putting Your Physical Address On Each Page Help With Local SEO?
Will putting your store’s address in the footer of your web page help with your site’s local SEO?
Yes it will.
At the very least you are going to be ensuring that the name of your town is included as text on each page on your site.
It will also help to build trust from your visitors too.
[Tweet “Put your address on each page to help with local SEO”]Should Your Site Contain A Privacy Policy?
Does google consider sites with a clearly stated privacy policy more trustworthy and give them a rankings boost?
Brian Dean certainly thinks so (point 72 on this awesome list of ranking factors).
I am not so sure, however, to ensure your site is covered legally (in most countries) a privacy policy is something that you will need. It is also something that some visitors will look for before passing over their data + you will need one if you want to add adsense ads to your site at any point.
So while I am not convinced it will have any SEO benefit, a privacy policy is something your site should definitely have.
Can Google Follow Javascript Links?
Think you can use javascript links to hide pages/external links from google?
Google is now very capable of following links in javascript and indeed interpreting javascript.
Can Adsense Ads Hurt Your Rankings?
Google will not penalise your site for using adsense ads (why would they, it’s a revenue earner for them), but as I mentioned in earlier, the ads should be secondary to the pages content and not dominate/be intrusive.
Will Google Cap The Amount Of Organic Traffic Your Website Receives Each Day?
As your website grows you will find that at various points traffic from google is reasonably consistent from day to day, i.e. it seems to plateau. For example you might receive 100 visitors a day, 200 or whatever.
This has led to the belief that google actually puts a cap on the amount of traffic that your website receives in a day from particular queries, so when you reach that imposed daily ‘limit’ you won’t show up in the search results for that query any more (on that day).
Is this the case?
Well, there is a very lengthy discussion on the topic of traffic throttling on this webmaster world thread started in 2010 and a lot of webmasters certainly think it is the case.
However, the question of whether there is anything in the algorithm to ‘throttle’ traffic has been posed to googlers on a number of occasions and they have clearly stated that there is nothing that would specifically cause this.
This article from Michael Martinez does any excellent job of explaining why it often appears that google is throttling traffic and why it should be discounted. I agree with his view.
Will Alt Text On Images Help Your Rankings?
Adding accurate, descriptive alt text to your images is definitely good SEO practice.
This used to be particularly effective for bringing in traffic from google image search, but since the image search interface changed a while back it is not such a great source (see this post on webmaster world).
Still, adding alt text to your images is almost certainly a piece of the overall SEO pie and is likely to give some sort of boost (however small) to a pages overall SEO. So do it!
Can Google Read CSS?
Are you putting a load of text content in a div and then using CSS to push it off screen?
I suggest you stop. Now.
Google can definitely read css, almost certainly does and will likely penalise your site for any dodgy tricks. They’ve been doing this since at least 2005.
Do Dot Com Sites Rank Higher Than Country Specific Domains?
Dot com is still the domain extension most users will most readily identify with for a web address and some SEOs believe that .com sites will rank higher than country specific extensions.
It would certainly appear that dot com sites have more of a chance of showing up worldwide than say a .ru site showing up in UK results. This post by Matt Cutts (and subsequent detailed discussion in the comments) is well worth a read.
If you are targeting worldwide you probably want to grab a dot com, but if you are targeting your business more locally then you might be best with a country specific extension. The safest option of course is to grab both.
Note: You can also set location targeting in webmaster tools, which is always good practice.
Does Google Prefers Web Pages With A .Html Extension?
Google has absolutely no preference for file extension, all it cares about is whether your content is crawlable and indexable.
Matt Cutts has spoken directly on this here (the quote below sums it up).
Sometimes at a conference people will ask me “Does it matter what extension I use for my pages? Does Google prefer .php over .asp, or .html over .htm?” And my answer is “We’re happy to crawl all of these file extensions. It doesn’t matter what you choose between any of those.”
So no preference for .html extension, or indeed any extension in particular, although he does advise to steer clear of .exe (but hopefully that goes without saying!).
Will Google Read Your Gmail To Find Out What You Are Up To?
Setting aside post Snowden/Prism paranoia, I am pretty certain that google (specifically their webspam team) will not read your emails and use anything they find in there against your site.
I’m going to go ahead and say that this is false though.
Clickthrough Rate (Ctr) From Search Results Is Used As A Ranking Factor
Do google take clickthrough rate into account when ranking web pages?
Again, there is a divide in the thinking of SEOs on this one.
Brian Dean included CTR in his list of ranking factors (linked above, but here it is again) and there are lots of other articles which say similar (this is an interesting one from back in 2011).
The problem for me though is that this would be an easy one to manipulate. Just pay some team in some far flung corner of the world a bit of cash for going through and clicking on your result in the SERPs and see it shoot up the rankings.
So, I personally don’t think that this is a ranking factor (at least not one of any significance), but as there is a divide I will leave it as unconfirmed. I guess if a particular result never received any clicks then this might be a sign that it didn’t belong there.
Obviously, notwithstanding any direct SEO benefit you want to make sure that your result is as attractive as possible (well written title, meta description etc) to maximise traffic.
Is Length Of Domain Registration A Ranking Factor?
By length of domain registration here I mean when a domain expires, i.e. renewing domains year to year as opposed to going for a ten year registration.
The argument is that registering a domain for a longer period shows commitment, which could be a trust signal.
I have not been able to find anything conclusive on this, but I normally register for 2 years maximum and have never had any issues with ranking sites, so if it is a factor it is probably a very small one.
Are Hyphenated Domains Best For SEO?
Here is what Moz has to say about using hyphenated domains in their page on domain name best practices: –
If your domain name is two words (like www.examplesite.com), you may want to separate the words with a hyphen for readability: www.example-site.com. That said, use of hyphens also correlates highly with spammy behavior—and more than one hyphen should not be used in a domain name. For this reason, it’s generally better to stick to domain names containing only one or two words.
I would agree with that. Before the exact match domain update, domains such as very-specific-niche-search-term.com were commonplace, but they are not exactly user friendly.
When giving out your web address verabally you will also find that a lot of people don’t know the difference between a hyphen, an underscore a forward slash etc, so I tend to avoid them in most instances.
This is an interesting test which appears to show all other things being equal, non hyphenated domains will actually outrank hyphenated ones.
Are Hyphenated Urls Best For Individual Pages?
Page specific URLs on the other hand are a different story.
Matt Cutts has been quoted directly advising the use of hyphens (or dashes) as word separators (more here).
“If you are going to make a site and you’re starting fresh, so you’ve got a blank slate to work with, I would probably go ahead and go with dashes. I would continue to go with dashes at lease for the foreseeable future.”
“Nobody’s slated to be working on that so at least for the time being it’s better to use the dash.”
In my opinion hyphenated page urls also look best in the SERPs and are more likely to be clicked.
So, best SEO practice for page urls is to use hyphens to separate words.
[Tweet “Hyphenated URLs are best for #SEO”]Are Short Urls Better For Rankings?
Are short URLs likely to outrank longer URLs?
Well, while I don’t believe you will be penalised specifically for longer URLs (unless you are stuffing in keywords), or that you will get any direct boost for shortening a URL, shorter URLs certainly look neater in the SERPS and are more ‘shareable’.
Personally I like to go for 2/3 word urls (separated with a hyphen of course!) with a couple of the most relevant keywords for the page/article. Copyblogger do this well (like most things they do).
So, I do not believe there is any specific benefit, but would still recommend shorter URLs where possible as a best practice.
Is Including Your Brand Name In Your Page Titles Good For SEO?
This is something I have actually changed my mind on recently (SEO is a constantly evolving animal!).
My general advice used to be to include your brand in your page titles, after the main keywords/phrase/page name.
These days however google will automatically add your site’s name/brand to most SERPs (you can read more about that here), so I have come round to the opinion that there is no longer a real need to include your brand/site name in your title tag and now tend to just use the page name/product for the title tag.
Do You Need X Number Of Links To Rank?
No need to labour on this one.
If someone tells you that to rank your page you need x number of links then they are talking nonsense. As we have already discussed above not all links are created equally, so one link (of the right kind/power) can often do more for your site’s rankings than 1,000 low quality ones.
[Tweet “There is no magic number when it comes to links.”]Is There More Traffic To Be Had From Longtail Searches Than Main Keywords?
I have covered this in detail in a previous article, which you can read here.
To summarise the article, I have always found the bulk of my traffic comes from long tail phrases, even when I am ranking highly for what would be considered the main keywords/phrases in a niche.
I also noticed an increase in traffic to lengthy, detailed articles after Google’s hummingbird update.
The real traffic is absolutely in the long tail!
Should You Limit The Number Of Links On A Page To 100?
This is another piece of SEO advice which is outdated.
Google’s webmaster guidelines used to advise keeping the number of links on a page to a ‘reasonable number (less than 100)’.
However, Matt Cutts wrote a blog post on this back in 2009 advising that this advice (which was originally based on the fact that google would only index 100kb per page) was no longer a hard and fast SEO rule.
It is of course true that the more links on a page, the less pagerank will be passed by each link, but like most things in SEO these days, user experience trumps the technical side, so if your page needs 200 external links then go for it!
How Often Does Google Update Their Index?
Old school SEOs will remember the infamous ‘google dance’.
Roughly once a month, google would update their index and search rankings would jump around for a couple of days before stabilising.
This is very much a thing of the past and these days google updates their index/rankings continually. You can expect to see changes you have made to your site take effect as soon as the page/pages have been re-cached and new inbound links (potentially) give a boost when they are spidered.
Over To You!
So, there we go! Some of the answers have been more clear cut than others, so if you disagree with any of my conclusions then please feel free to let me know by leaving a comment.
Hopefully this list will serve as a good reference point for anyone looking to know more about SEO in 2014. I would also hope that there is something for everyone here, whether you are an SEO noob, or a veteran like myself.
I spent a lot of time on putting it all together and have tried to find different view points on each point on the list before coming to conclusions (except where the answers are totally clear cut).
As always, I would love to hear your thoughts/questions, so please leave a comment below and would also be grateful if you could help me share the article by giving it tweet, like etc.
[Tweet “SEO In 2014: The Big Fat Guide”]Join my free mailing list below for more regular white hat SEO tutorials and tips and if you would like help with your site’s SEO then I offer a range of SEO consultancy services.
For more SEO tips, check out my post on Ahrefs 100+ SEO Tips.
[bigsignup]